Feature Story – By Juliana Ciccarelli and Kevin Millar
 As remote and hybrid work transform the employee experience, life sciences companies need to be asking themselves, “How can we make learning more accessible, engaging and personal?”
As remote and hybrid work transform the employee experience, life sciences companies need to be asking themselves, “How can we make learning more accessible, engaging and personal?”
Within the learning and development (L&D) industry, leveraging the latest technological innovations to create engaging experiences is not a new trend; however, educational and training initiatives and the creative ways in which they are applied hold the greatest opportunity for increased value in the future.
In this article, we explore the indicators and trends that will shape life sciences learning and training over the next few years. Each approach existed pre-COVID, but with the increased prevalence of work-from-home, they have been accelerated (and in some cases pivoted) to adapt to the new way in which we work. Here, we’ll dissect these emerging approaches from a general view and touch on considerations for the new hybrid model of working.
Personalized Flexibility
An emerging shift in the workforce, resulting from the pandemic, is the desire for flexibility and personalization in multiple facets of life. This has increased the expectation that organizations must incorporate more choices for employees to retain valuable talent.
Within L&D, prepandemic programs were often designed around a one-size-fits-all learner journey, where individual preferences and learning needs came second to the business need for training. We are now seeing that the L&D space is being disrupted the same way as the physical office environment.
L&D teams are being asked to rise to the newly realized needs and expectations of their employees, by utilizing the same agility and flexibility displayed by both the organization and the individuals regarding remote work. Organizations must offer learner driven journeys and asynchronous models to support the flexible schedules and locations of each employee. The following approaches discuss support for this hybrid world and what we envision happening over next few years as the employee learning experience continues to evolve.
High-Fidelity Simulation Training
High-fidelity simulation training is an education methodology that involves using sophisticated life-like scenarios and environments where trainees learn through experiencing hyper-realistic exercises. This form of application-based learning provides a close-to-real-world experience, mimicking on-the-job tasks that allow learners to make better decisions when faced with these scenarios in real life.
Investing in high-fidelity simulation training can look like many things. It may take the form of virtual reality (VR) or conversation simulators. These formats help bridge the emerging gaps in experience that arise from a decrease in actual face-to-face opportunities, ensuring that when they do occur, teams are prepared and polished. Simulations also build and retain soft skill sets, including empathy, an especially important skill in healthcare, that can be lost with less in-person dialogue.
Simulation training is a tactic well-suited for all levels of learners as they progress through their learning journey. However, it also benefits high performers, helping them build mastery-level skill sets — often a difficult group to retain, refine and engage. As innovative technologies such as VR and augmented reality (AR) become more affordable and accessible, and live event participation remains more selective by those attending, we expect to see increased investments in highfidelity learning simulators to make those moments as impactful and memorable as possible.
Multi-Modal Digital Learning Modules
Multi-modal digital learning seamlessly integrates several forms of visual and interactive digital media into one learner experience. This format offers a balanced and engaging learning experience as it is widely accepted that students learn best through multisensory approaches to subjects.
From the micro (module) and macro (curriculum) level, this includes a suite of potential media options, such as video, animation, quizzes, activities, AR, VR and 3-D models. Based on the distinct learning moments each one provides, these formats work together to create a memorable learning experience for improved recall.
Learning modules that combine different media types offer the promise of effectively training a broad audience by selecting the ideal media for each bitesized module to optimize learning and increase engagement. Over time, elearning programs will build libraries of proven and successful module structures where users can customize their own learning journey. This will lead to more personalized learning journeys that are specific to an individual’s preferences, knowledge gaps and interests.
To make this a reality, digital literacy and accessibility must be considered for these programs to be implemented and universally impactful. Teams often display a wide range of digital experience, so it is critical to ensure that all members feel comfortable with the tools being offered.
Consider developing user guides, offering training sessions and tutorials that assist with successful adoption. With many people accessing content from remote locations, access via high-bandwidth internet cannot always be assumed. It is important to develop media assets that are optimized for all types of connections. This will ensure that the quality of experience remains consistent for all learners.
Storytelling for Empathy
Narrative-based learning is an optimal training technique to humanize content, engage learners and connect them to the subject matter. Weaving storytelling and different perspectives into scientific learning enhances reflective thinking, which can lead to more empathetic decision-making, interactions and communication.
Storytelling’s presence in L&D is evolving beyond simply communicating the user journey and is being incorporated into more content-heavy areas to refine data and characterize information. As we begin to build more story-centric experiences for omnichannel and multichannel worlds, adapting story formats to fit appropriately with differing channels is essential. This ensures that the story remains both impactful and easy to follow, while balancing the sensitivity of the content.
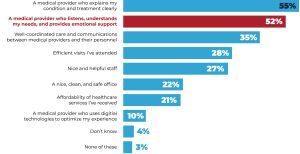
If we look at the life sciences industry specifically, teaching emotional support is just as important as medical support. In a recent study by Accenture, 52% of patients said having a provider who listens, understands patient’s needs and provides emotional support is an important factor in creating a positive experience with a healthcare provider. (See Figure 1.)
Currently, a gap exists between these two groups as physicians must translate from a data-centric and scientific format to a more personal and empathetic one. The disconnect between content retention and delivery leaves healthcare providers (HCP) with the burden of adapting their approach when applying data into practice. Pharmaceutical companies are presented with a great opportunity to modify their style of sharing to meet HCPs’ needs and focus on storytelling delivery for training.
Collaborative Peer-to-Peer Programs
Peer-to-peer (P2P) programs have been an integral concept in many learning programs to build trust, community and understanding. Traditionally, P2P programs share information one way — from facilitator to attendee — creating a clear divide between learner and expert. Although often effective, we are now seeing a shift to a more collaborative P2P approach and the emergence of workshops, trainthe-trainer activities and ideation sessions. By removing the divide between expert and learner, space is created for what scholars call social or collaborative learning.
This style of learning is rooted in problem-solving and discussionbased activities, rather than didactic learning. This approach encourages diverse views about topics, offering the host organization a channel for organic feedback. This feedback can then funnel back into strategic discussions around positioning, while also creating more engaging and memorable moments as attendees have been active participants.
Physically present sessions offer natural moments of discussion, before and after the presentation, even if not built directly into the agenda. Virtual sessions should be elevated to promote collaboration in a more structured format using collaborative P2P online tools that create two-way communication moments to educate and foster conversation.
Virtual collaborative workspaces, such as real-time whiteboards like Miro and Mural, make solutioning and strategizing an engaging and collaborative exercise. Tools such as Brainly and Figure 1’s Medical Case forums stimulate thinking by tapping the community for knowledge sharing. Even VR can be used to build a space for shared understanding that promotes peer interaction with conversation prompts following.
P2P programs remain a critical tool in education and hint at a future where the paradigm shifts from oneway to two-way learning. Future peer sessions will be more collaborative with built-in solutioning exercises, interactive media designed to foster conversation and outlets at all stages of the process to create continuous learning opportunities for both the attendees and the facilitator.
Conclusion
The post-COVID workplace will require L&D solutions that are engaging, accessible and able to deliver personalized learning. So how do we get there?
While innovation and adaptability are not new to L&D, swiftly adapting curriculums for hybrid learning may not be mainstream for many organizations. In the rush to adapt to working from home, there may be substantial areas where “good enough for now” solutions early in the pandemic became the new standard.
Whether it’s implementing innovative technologies, collaborative learning or dynamic, customizable training, organizations must examine how best to reach learners, by auditing the technology and its impact, as well as engaging users and teams about their experiences so far.
Working from home is likely to continue for many; however, finding ways to implement strategies that offer real-world experiences, personalization and interactive technology will be key for active learning success. Building on those successes will create a more engaging and resilient system for the years to come.
Juliana Ciccarelli is creative director at Red Nucleus and Kevin Millar is senior vice president of creative & medical science at Red Nucleus. Email Juliana at jciccarelli@rednucleus.com and Kevin at kmillar@rednucleus.com.